Federal Reserve Hikes Interest Rates 0.25% – Expects More Increases to Come
The Federal Reserve Wednesday’s benchmark interest rate increase was one quarter point. There is little to indicate that the hiking cycle is over.
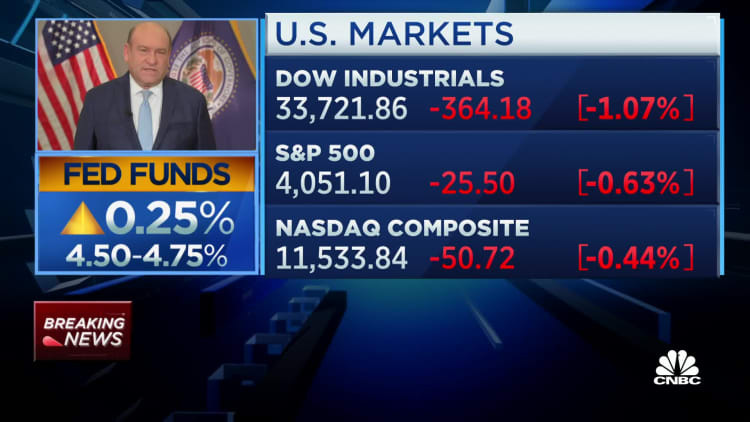
In line with market expectations, Federal Open Market Committee raised the federal funds rate 0.25 percentage points. This brings it to 4.5%-4.75% target, which is the highest rate since October 2007.
This was the eighth increase in a series that started in March 2022. It is the rate that banks charge each other to overnight borrow money. But it also sets the funds rate. This can be used to create consumer debt products.
The Fed targets inflation increases to lower it, which, despite recent signs that it is slowing down, is still at its highest point since the 1980s.
The a?href=”https://www.cnbc.com/2023/02/01/heres-what-changed-in-the-new-fed-statement.html”>post-meeting Statement Not to be confused with inflation “has eased somewhat but remains elevated,” A slight modification to the previous language.
The markets, however, were watching this week’s meeting for signs that Fed would end rate increases soon. The statement didn’t provide such signals. At first stocks fell In the wake, the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell more than 300 point.
It also included language noting the FOMC’s continued belief in the necessity for “ongoing increases in the target range.” Participants in the market had hoped for a softening of this phrase but the statement, which was unanimously adopted, retained it.
One part of the statement was changed when it described what would determine the future policy direction.
Officials stated They would make the final decision. “extent” Rate increases in the future will be determined by factors like the effect of rate hikes on the economy, the lags and financial conditions. The statement stated previously that the rate would be determined using these factors. “pace” The committee may give a nod to future hikes.
In 2022 the Fed approved four consecutive 0.75 percent point moves, before moving to a smaller 0.5 percent point increase in December. Recent Public statementsMultiple officials stated that they believe the central bank can at least reduce the magnitude of hikes without indicating when they might end.
It was raising its benchmark interest rate but the committee defined economic growth as “modest” It did not mention that there was unemployment. “has remained low.” The latest job market assessment did not include any language regarding employment gains. “robust.”
The Fed continues to fight inflation and the statement is unchanged from previous messages.
Fed remains focused on inflation
Fed policy is thought to work on a lag – when the central bank raises rates, it takes time for the economy to adjust to tighter controls on money.
This particular round started because of CovidThese are correlated factors like clogged supply chain and a rising demand for goods and services. The war in Ukraine Rising gas prices were exacerbated by unprecedented fiscal stimulus that fueled rising costs for a wide range of goods and services.
The past year has seen a rise in food prices of more than 10%. Only eggs have seen a 60% increase in pricesAccording to Labor Department data, butter prices have increased more than 31%, and lettuce prices have risen 25% since December. The gas prices started to fall towards the end of 2022, but they have risen in recent days to $3.50 per gallon nationwide, an increase by about 30 cents over the month prior, according AAA.
Although Fed officials remain determined to tackle inflation, they admit that recent data shows pressures could be decreasing. The Consumer price index fell 0.1% in December on a monthly basis and is up 6.5% from a year ago – down from the peak of 9% last summer but still well above where the Fed feels comfortable.
Fed buys bonds
The Fed has been reducing its bond portfolio in addition to rate increases. This has led to a decrease of $445 billion in bond portfolio holdings since June. The Fed is targeting a level of $95 Billion in maturing bonds, which it allows to roll off each month instead of reinvesting.
According to the San Francisco Fed the balance sheet reduction is equivalent to approximately 2 percentage points additional rate increases. The balance sheet remains at over $8.4 trillion.
The Fed’s decision to end these increases is being watched closely by the markets.
At the December FOMC meetingCommittee members indicated that they saw the “terminal rate,” Point at which the Fed considers its policy too restrictive. The markets are betting that the number is closer than 4.75%. After a quarter-point increase in March, they expect the Fed will begin to reduce rates later in this year.
Stocks rose in 2023 because investors expected a looser Fed.
" Conservative News Daily does not always share or support the views and opinions expressed here; they are just those of the writer."







Now loading...